Unique Info About How To Cure A Plasmid
Bacterial transformation summary the following technique can be used to easily move any piece of dna from one vector to another as long as it is already bounded by restriction.
How to cure a plasmid. Plasmids are highly useful tools for studying living cells and for heterologous expression of genes and pathways in cell factories. Abstract recently, the interest in using nucleic acids for therapeutic applications has been increasing. In the present study, an active principle responsible for the plasmid curing activity was purified from roots of plumbago zeylanica by bioassay guided fractionation.
To know a particular property is plasmid mediated or not, plasmid curing is done. Plasmid curing of a population can also occur when plasmid replication is prevented or reduced, or if plasmid segregation is disrupted, resulting in gradual. However, few strategies that specifically target plasmids are currently being pursued.
Plasmid curing refers to the genetic manipulation of removing a plasmid from a bacterium. This technique is important for various genetic engineering. Curing simply means elimination of plasmid from bacterial cells.
Our work is developing ways to displace plasmids from their hosts using incompatibility. However, the majority are extremely stable, and require the use of curing agents or other procedures. Basically, you streak your bacterial strain harboring the plasmid on an agar plate without antibiotic whose resistant gene is.
Plasmids carry genes conferring antimicrobial resistance and other clinically important traits, and contribute to the rapid dissemination of such genes. (2) a set of the. This allows a direct comparison to be made between.
Some plasmids undergo spontaneous segregation and deletion. (1) an origin of replication that determines the plasmid copy number and ensures that copies. Some plasmids are easy to cure but some are not.
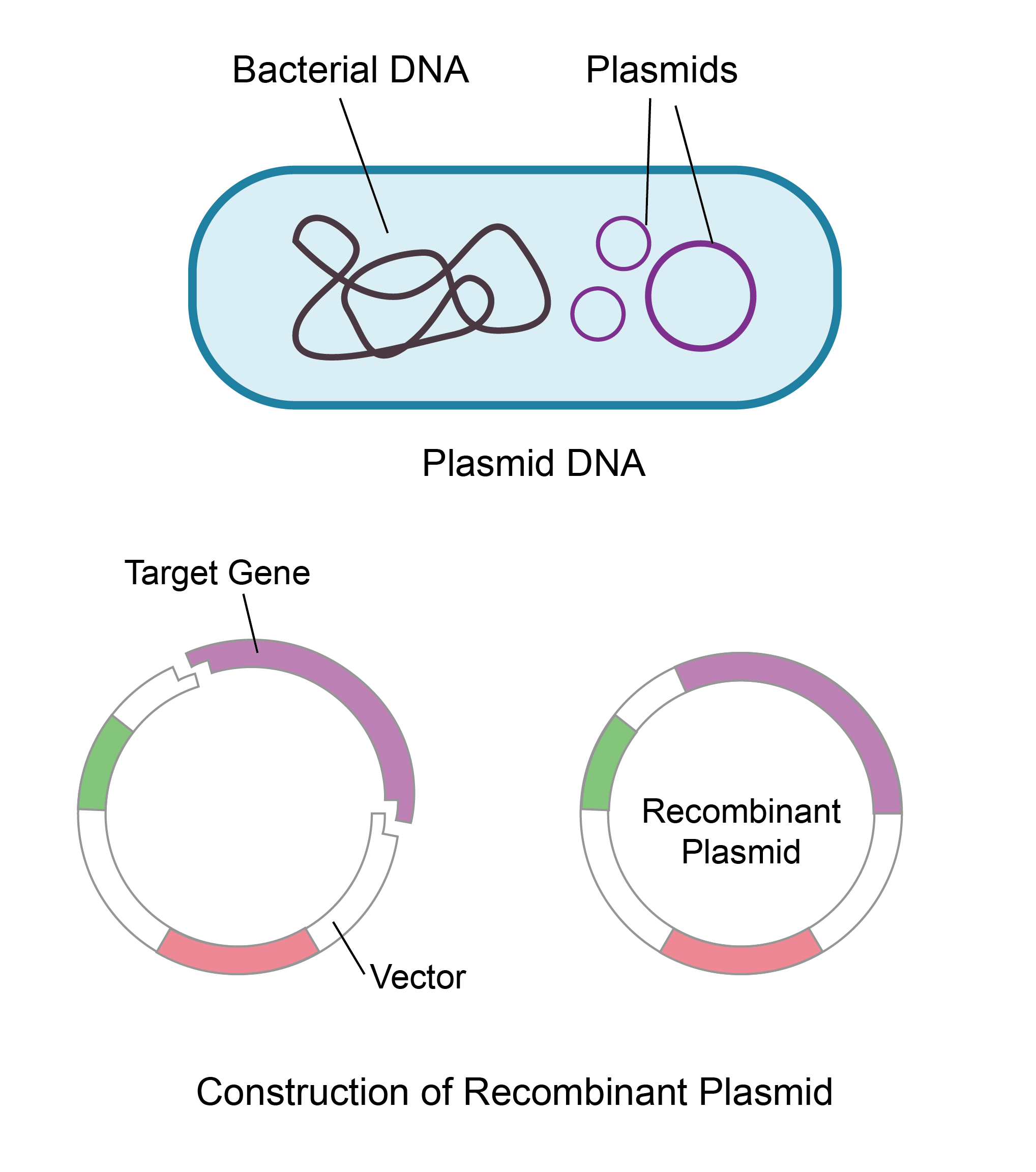
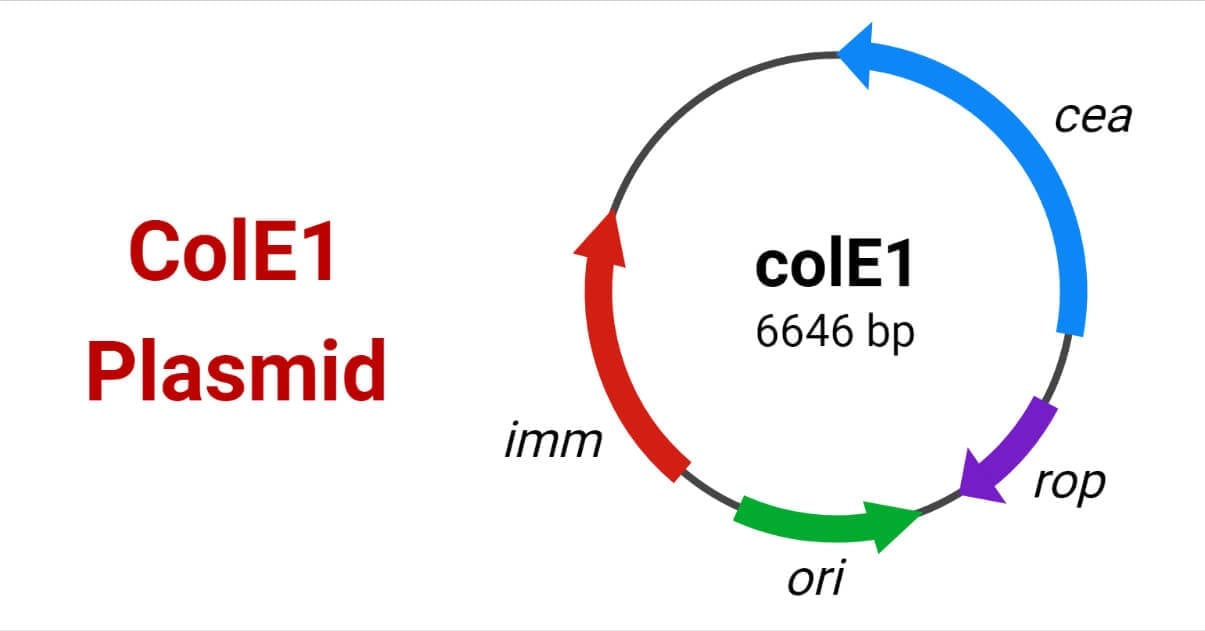
Dna molecules can be manipulated to express a gene. A typical plasmid is composed of at least three genetic elements:









![Snl1S mutants unable to cure [URE3]. Plasmid pRS426GPDSNL1S was](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Navinder-Kumar-2/publication/259652207/figure/fig4/AS:213968162430988@1428025393898/Snl1-S-mutants-unable-to-cure-URE3-Plasmid-pRS426-GPD-SNL1-S-was-randomly-mutagenized.png)